Adding more solute to a solvent
Adding More Solute To A Solvent. #i# is the van�t hoff factor that is approximately how many particles go into solution for every. It takes 6 hours to dry a wet solid from 50% moisture content to the critical moisture. And likewise, the freezing point of the solution. If we had pure water and added just a little bit of phenol to it at room temperature, we would find that it would dissolve into the water up to about 7 or 8 wt%.
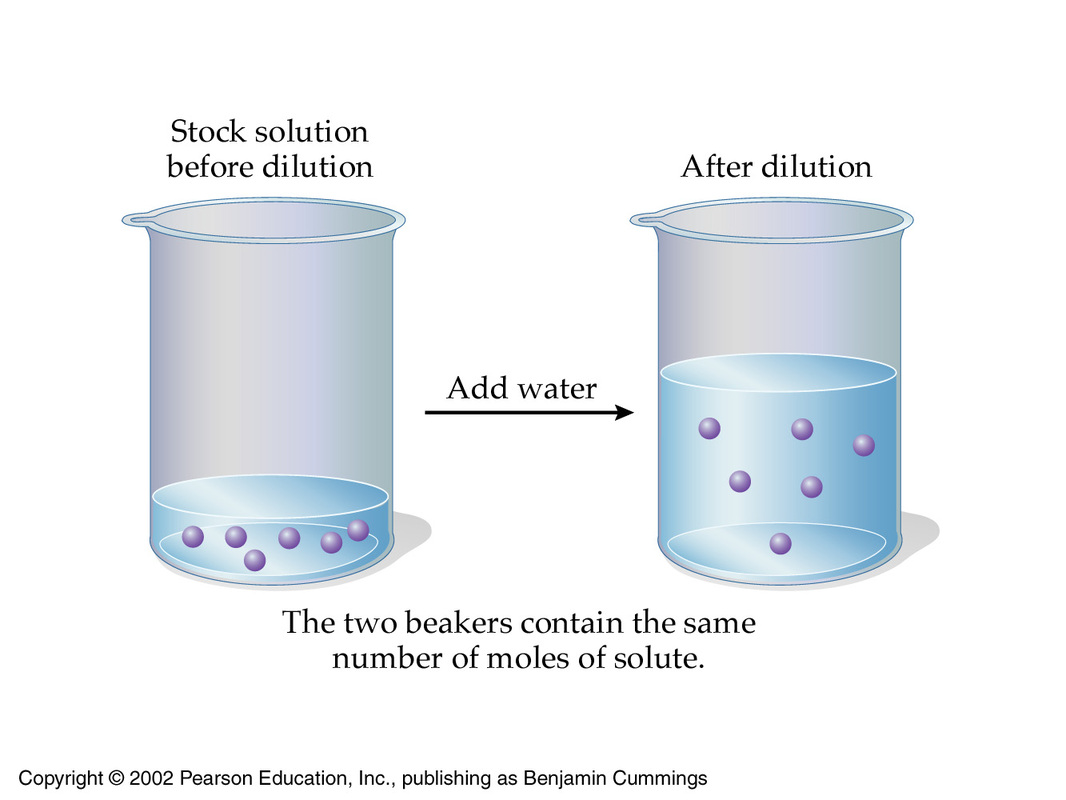 mL of solution has a concentration of 3.0 M. How much water needs to be From socratic.org
mL of solution has a concentration of 3.0 M. How much water needs to be From socratic.org
The presence of a large amount of solid solute will allow the solution to freeze but at a lower freezing point. Of course, #t_b# is the boiling point of the solution, and #t_b^*# is the boiling point of the solvent by itself. A solvents vapor pressure will lower when a solute is added. Increasing the solute would increase the concentration. Adding solute to a solvent will essentially dilute the solvent molecules, and according to raoult�s law, this leads to a decrease in vapor pressure. If you add more solute to a solution, does it turn into a solvent?
And by definition, a \text{saturated solution} is a solution that contains an amount of solute that is equal to that amount of solute that would be in equilibrium with undissolved solute.
For instance, if your lemonade was too tart, you would add more water to decrease the concentration. Increasing the solute would increase the concentration. The solvent crystallizes pure, leaving the solute outside of. 1) by boiling away the solvent. There is a region, defined by the rainbow shape in the diagram above in which phenol and water separate into two distinct phases. Adding more solute increases the concentration of solute in the solution (raises the solution’s molarity).
Source: quora.com
Under equilibrium conditions, nothing at all will happen. What happens when you add more solute to an unsaturated solution? If we had pure water and added just a little bit of phenol to it at room temperature, we would find that it would dissolve into the water up to about 7 or 8 wt%. The inlet rate of the solution containing a is 200 moles of b/hr.m2 and the solvent flow, rate is 400 moles of s/m2. A solvents vapor pressure will lower when a solute is added.
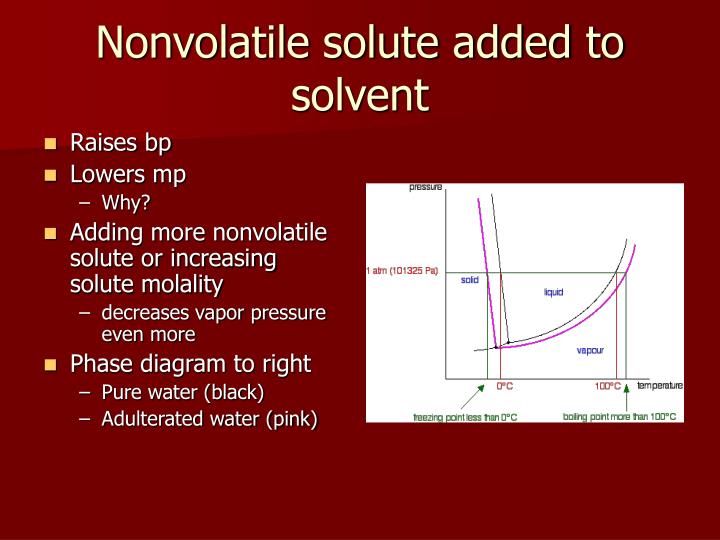 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
If we had pure water and added just a little bit of phenol to it at room temperature, we would find that it would dissolve into the water up to about 7 or 8 wt%. There is a region, defined by the rainbow shape in the diagram above in which phenol and water separate into two distinct phases. For instance, if your lemonade was too tart, you would add more water to decrease the concentration. What happens when you add more solute to an unsaturated solution? If your tea was too bitter, you could add more sugar to increase the sweetness.

Adding solvent will make a solution more diluted. Changing the amounts of solute and solvent directly. A solvents vapor pressure will lower when a solute is added. Stirring the solution will simply increase the rate of dissolution, but not the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved. What happens when you add more solute to an unsaturated solution?
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Increasing the solvent would decrease the concentration. At some point, the solution will be saturated (hold as much solute as it can). • brute force, or gravimetric. The change (volume decrease or volume increase of final solution) of volume depends of solvent and solute chemicophysical properties, e.g. If your tea was too bitter, you could add more sugar to increase the sweetness.
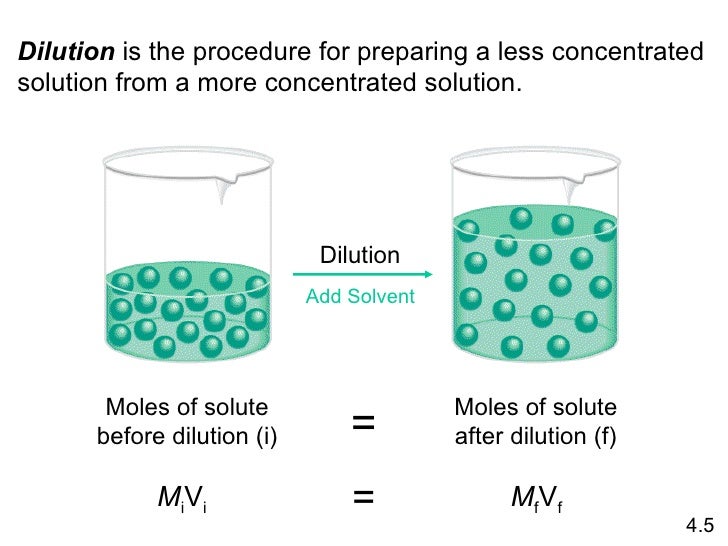 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Adding solvent will make a solution more diluted. If we had pure water and added just a little bit of phenol to it at room temperature, we would find that it would dissolve into the water up to about 7 or 8 wt%. Under equilibrium conditions, nothing at all will happen. Take water (solvent) and dissolve salt into it. And by definition, a \text{saturated solution} is a solution that contains an amount of solute that is equal to that amount of solute that would be in equilibrium with undissolved solute.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
#i# is the van�t hoff factor that is approximately how many particles go into solution for every. The solvent crystallizes pure, leaving the solute outside of. The change (volume decrease or volume increase of final solution) of volume depends of solvent and solute chemicophysical properties, e.g. If the solute is a gas, boil away the solute, then dissolve it again in less solvent. Assuming the solvent is volatile and the solute is not, one can take a carefully measured.
 Source: blinklearning.com
Source: blinklearning.com
For instance, if your lemonade was too tart, you would add more water to decrease the concentration. Assuming the solvent is volatile and the solute is not, one can take a carefully measured. So, phenol would be the solute and water the solvent. By adding more solute b. At this point adding more solute will not change the concentration of the solution.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Increasing the solute would increase the concentration. At some point, the solution will be saturated (hold as much solute as it can). Take water (solvent) and dissolve salt into it. The inlet rate of the solution containing a is 200 moles of b/hr.m2 and the solvent flow, rate is 400 moles of s/m2. If your tea was too bitter, you could add more sugar to increase the sweetness.
 Source: msjschemclass.blogspot.com
Source: msjschemclass.blogspot.com
Under equilibrium conditions, nothing at all will happen. Compound a is extracted from a solution of a b into a pure solvent s. The presence of a large amount of solid solute will allow the solution to freeze but at a lower freezing point. • brute force, or gravimetric. If the solute absorbs light at a wavelength where.
 Source: differencebetween.com
Source: differencebetween.com
Adding more solute increases the concentration of solute in the solution (raises the solution’s molarity). And by definition, a \text{saturated solution} is a solution that contains an amount of solute that is equal to that amount of solute that would be in equilibrium with undissolved solute. The change (volume decrease or volume increase of final solution) of volume depends of solvent and solute chemicophysical properties, e.g. Think of it this way. The solvent crystallizes pure, leaving the solute outside of.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
The change (volume decrease or volume increase of final solution) of volume depends of solvent and solute chemicophysical properties, e.g. Under equilibrium conditions, nothing at all will happen. 100 ml solution having 50ml solute b. A solvents vapor pressure will lower when a solute is added. Changing the amounts of solute and solvent directly.
 Source: writeopinions.com
Source: writeopinions.com
Take water (solvent) and dissolve salt into it. The presence of a large amount of solid solute will allow the solution to freeze but at a lower freezing point. If we had pure water and added just a little bit of phenol to it at room temperature, we would find that it would dissolve into the water up to about 7 or 8 wt%. As stated in the previous posts, i believe that the addition of the solute, in this case, would only alter the volume of the solution ever so slightly so you shouldn�t worry too much about it! The dissolved solute will be in equilibrium.
 Source: fineartamerica.com
Source: fineartamerica.com
Solute almost always changes the volume of final solution. At this point adding more solute will not change the concentration of the solution. If the solute is a gas, boil away the solute, then dissolve it again in less solvent. Think of it this way. Take water (solvent) and dissolve salt into it.
Source: quora.com
Adding more solute will simply result in more solid at the bottom of the solution. For instance, if your lemonade was too tart, you would add more water to decrease the concentration. The solvent crystallizes pure, leaving the solute outside of. Think of it this way. If the solute absorbs light at a wavelength where.

The inlet rate of the solution containing a is 200 moles of b/hr.m2 and the solvent flow, rate is 400 moles of s/m2. The inlet rate of the solution containing a is 200 moles of b/hr.m2 and the solvent flow, rate is 400 moles of s/m2. The effect of adding a solute to a solvent has the opposite effect on the freezing point of a solution as it does on the boiling point. At this point adding more solute will not change the concentration of the solution. At some point, the solution will be saturated (hold as much solute as it can).
Source: socratic.org
For instance, if your lemonade was too tart, you would add more water to decrease the concentration. Boiling point elevation occurs as follows:. The solvent crystallizes pure, leaving the solute outside of. If the solute absorbs light at a wavelength where. So, phenol would be the solute and water the solvent.
 Source: proprofs.com
Source: proprofs.com
100 ml solution having 50ml solute b. 100 ml solution having 50ml solute b. If you add more solute to a solution, does it turn into a solvent? • brute force, or gravimetric. If your tea was too bitter, you could add more sugar to increase the sweetness.
Source: quora.com
And by definition, a \text{saturated solution} is a solution that contains an amount of solute that is equal to that amount of solute that would be in equilibrium with undissolved solute. At some point, the solution will be saturated (hold as much solute as it can). And by definition, a \text{saturated solution} is a solution that contains an amount of solute that is equal to that amount of solute that would be in equilibrium with undissolved solute. Adding solvent will make a solution more diluted. Increasing the solvent would decrease the concentration.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title adding more solute to a solvent by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





