Bronsted lowry acid and base examples
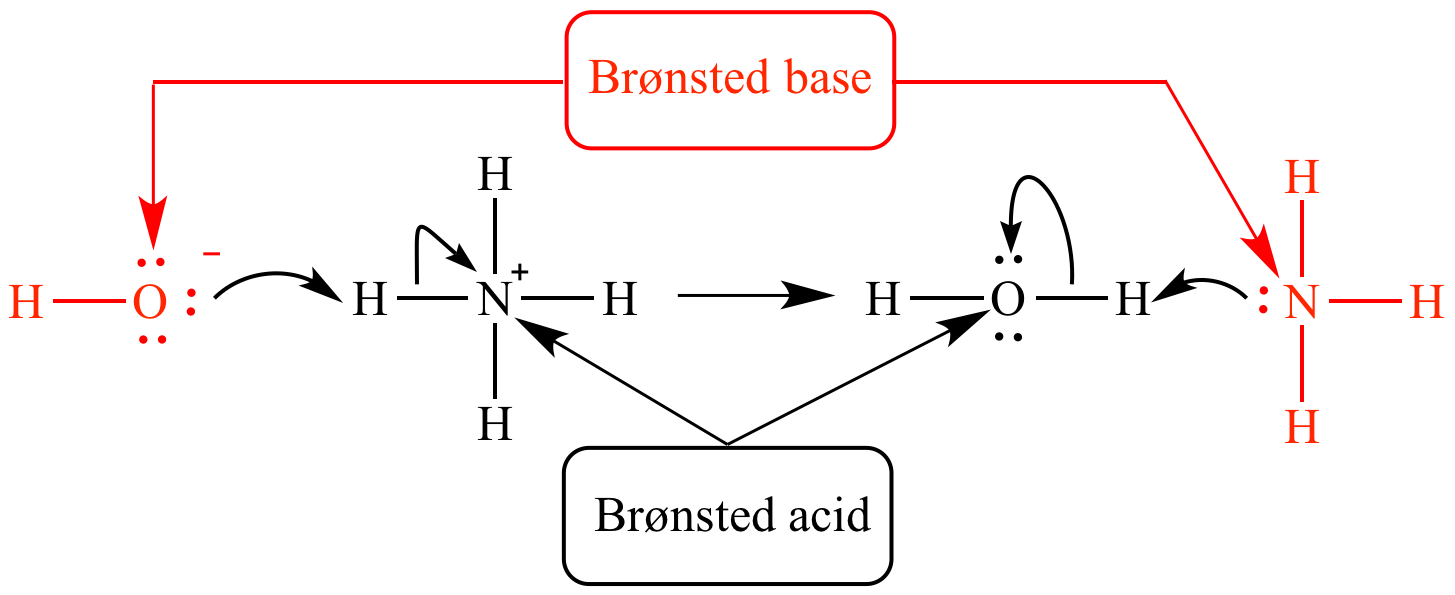
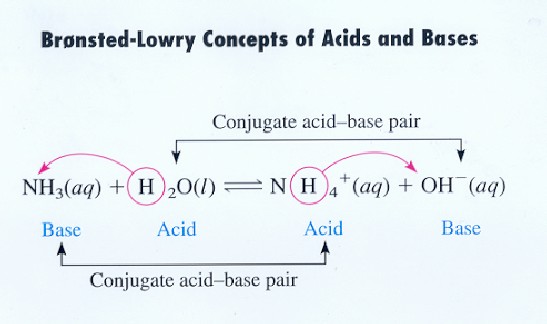
Bronsted Lowry Acid And Base Examples. When it donates its proton, the acid becomes its conjugate base. A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. When robert boyle characterized them in 1680, he noted that acids dissolve many substances, change the color of certain natural dyes (for example, they change litmus from blue to red), and lose these characteristic properties after coming into contact with alkalis (bases). In the image shown at the right one molecule of h 2 o acts as a base and gains h + to become h 3 o + while the other acts as an acid and loses h + to become oh −.
 BronstedLowry Acids and Bases ( Video ) Chemistry CK12 Foundation From ck12.org
BronstedLowry Acids and Bases ( Video ) Chemistry CK12 Foundation From ck12.org
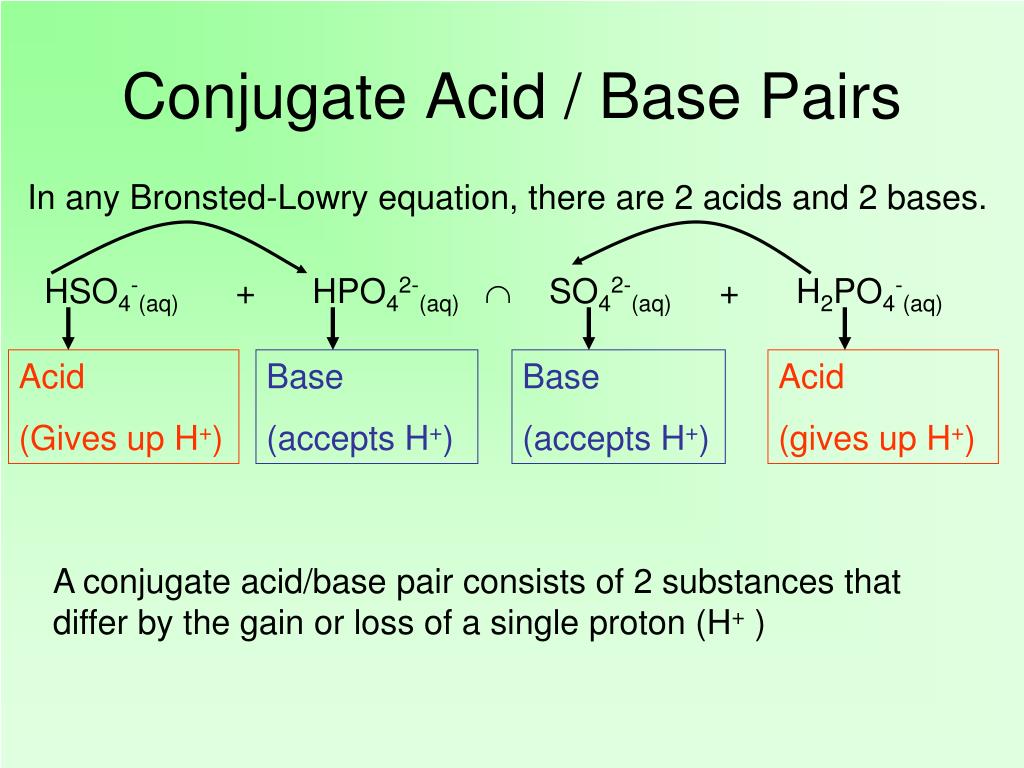
H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−. Consider the prototypical arrhenius acid. The extra electron gives hydroxide. In short, acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Bjerrum in denmark and t.
A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor.
Examples of electrons are bronsted lowry acid and bases examples. When robert boyle characterized them in 1680, he noted that acids dissolve many substances, change the color of certain natural dyes (for example, they change litmus from blue to red), and lose these characteristic properties after coming into contact with alkalis (bases). How can you tell if its a bronsted base? ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Examples of electrons are bronsted lowry acid and bases examples. When it donates its proton, the acid becomes its conjugate base.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Consider the prototypical arrhenius acid. Examples of electrons are bronsted lowry acid and bases examples. So is nh 3 an acid or base? A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. In the image shown at the right one molecule of h 2 o acts as a base and gains h + to become h 3 o + while the other acts as an acid and loses h + to become oh −.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
H 2so4(aq) +h 2o(l) → h 3o+ = h so− 4 (aq) h 2so4 donates a proton, making it an acid. In short, acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. Take the following reaction for example: Lowry in england independently proposed a theory known as ‘the proton theory of acids and bases’. Acids and bases have been known for a long time.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In the image shown at the right one molecule of h 2 o acts as a base and gains h + to become h 3 o + while the other acts as an acid and loses h + to become oh −. H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−. Acid substance which donate h are bronsted lowry acid. Chemicals that are acidic or basic are an important part of chemistry. Mineral deposits are the major supply of phosphorus.
 Source: chem.ucla.edu
Source: chem.ucla.edu
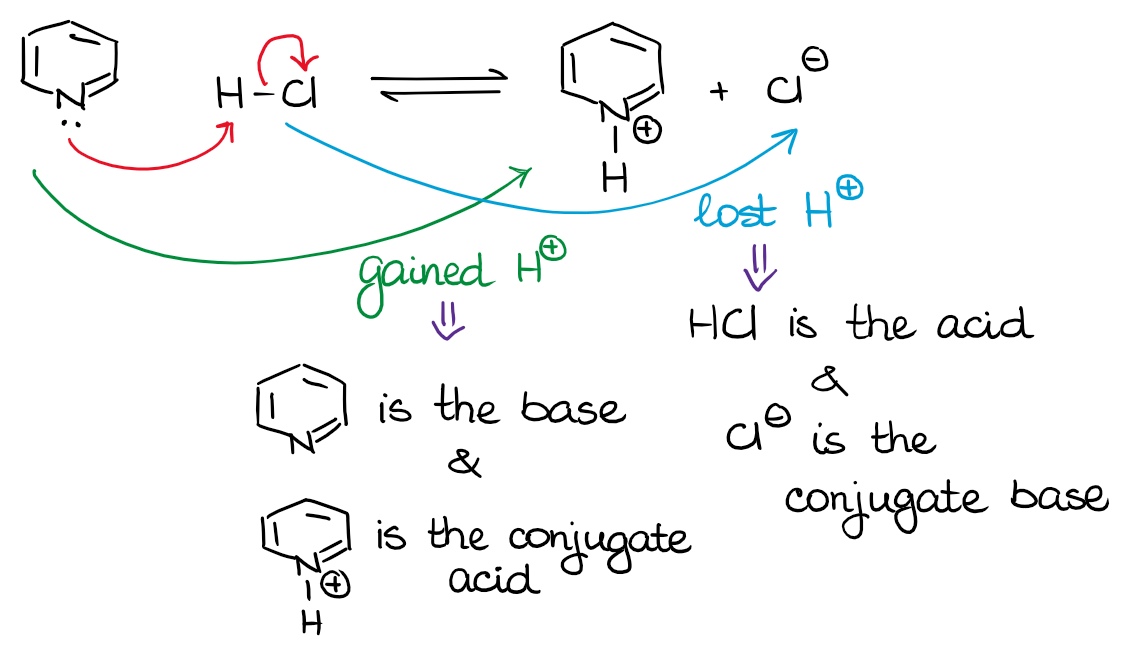
H c l + h 2 o h 3 o + + c l − is a acid n a o h n a + + o h − is a base Take the following reaction for example: In this reaction, a proton is transferred from hcl (the acid, or. How can you tell if its a bronsted base? H 2so4(aq) +h 2o(l) → h 3o+ = h so− 4 (aq) h 2so4 donates a proton, making it an acid.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. Bjerrum in denmark and t. H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−. H c l + h 2 o h 3 o + + c l − is a acid n a o h n a + + o h − is a base Well in 1923, two people with their last names bronsted and lowry defined acid as a substance which can donate a proton to form its conjugate base.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A more general look at the theory is an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor. Examples of electrons are bronsted lowry acid and bases examples. ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. The extra electron gives hydroxide. However, there were two scientists who independently proposed essentially the same theory about the definition of acids and bases.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
In short, acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. Mineral deposits are the major supply of phosphorus. ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Acids may be compounds such as hcl or h 2 so 4, organic acids like acetic acid (ch. In the eighteenth century, it was recognized that.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Lowry in england independently proposed a theory known as ‘the proton theory of acids and bases’. However, there were two scientists who independently proposed essentially the same theory about the definition of acids and bases. An acid is a proton donor, whilst a base is a proton. H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−. Take the following reaction for example:
 Source: ck12.org
Source: ck12.org
Bjerrum in denmark and t. Mineral deposits are the major supply of phosphorus. Consider the prototypical arrhenius acid. Cohen j, so the reaction goes to completion. H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Acids and bases have been known for a long time. ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. In this reaction, a proton is transferred from hcl (the acid, or. Take the following reaction for example: What makes a solution an acid?
 Source: chemistrylearner.com
Source: chemistrylearner.com
In 1923, johannes nicolaus bronsted and thomas martin. How can you tell if its a bronsted base? Another example is furnished by substances. When it donates its proton, the acid becomes its conjugate base. Consider the prototypical arrhenius acid.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
What makes a solution an acid? Consider the prototypical arrhenius acid. Mineral deposits are the major supply of phosphorus. H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−. In 1923, johannes nicolaus bronsted and thomas martin.
 Source: organicchemistrytutor.com
Source: organicchemistrytutor.com
Then, in contrast to arrhenius theory, silver chloride is present. Lowry in england independently proposed a theory known as ‘the proton theory of acids and bases’. The extra electron gives hydroxide. H c l + h 2 o h 3 o + + c l − is a acid n a o h n a + + o h − is a base When robert boyle characterized them in 1680, he noted that acids dissolve many substances, change the color of certain natural dyes (for example, they change litmus from blue to red), and lose these characteristic properties after coming into contact with alkalis (bases).
 Source: ck12.org
Source: ck12.org
Mineral deposits are the major supply of phosphorus. Another example is furnished by substances. H 2so4(aq) +h 2o(l) → h 3o+ = h so− 4 (aq) h 2so4 donates a proton, making it an acid. Cohen j, so the reaction goes to completion. Well in 1923, two people with their last names bronsted and lowry defined acid as a substance which can donate a proton to form its conjugate base.
 Source: library.tedankara.k12.tr
Source: library.tedankara.k12.tr
What makes a solution an acid? In 1923, johannes nicolaus bronsted and thomas martin. Examples of electrons are bronsted lowry acid and bases examples. In this reaction, a proton is transferred from hcl (the acid, or. Take the following reaction for example:
 Source: chemistrylearner.com
Source: chemistrylearner.com
What makes a solution an acid? When it donates its proton, the acid becomes its conjugate base. In the image shown at the right one molecule of h 2 o acts as a base and gains h + to become h 3 o + while the other acts as an acid and loses h + to become oh −. An acid is a proton donor, whilst a base is a proton. Likewise, a base is a substance which can accept a proton to form its conjugate acid.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Lowry in england independently proposed a theory known as ‘the proton theory of acids and bases’. ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Examples of electrons are bronsted lowry acid and bases examples. Well in 1923, two people with their last names bronsted and lowry defined acid as a substance which can donate a proton to form its conjugate base. Acid substance which donate h are bronsted lowry acid.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Bjerrum in denmark and t. H cl + n h 3 ⇌ n h + 4 + cl−. ( nh+4 ) is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia and the chloride ion ( cl− ) is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid. Well in 1923, two people with their last names bronsted and lowry defined acid as a substance which can donate a proton to form its conjugate base. When it donates its proton, the acid becomes its conjugate base.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title bronsted lowry acid and base examples by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.