Complications of acute myocardial infarction
Complications Of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Early reperfusion and medical therapy have drastically reduced ami Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins. Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction. Acute mechanical complications of mi include sequelae from left or right ventricular systolic impairment or a loss of structural integrity that results in cardiac wall rupture, papillary muscle rupture, or ventricular septal rupture.
 Management Principles in Myocardial Infarction Thoracic Key From thoracickey.com
Management Principles in Myocardial Infarction Thoracic Key From thoracickey.com
An acute myocardial infarction is a heart attack. Early reperfusion and medical therapy have drastically reduced ami Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (mi). The pathophysiological mechanism of mc post ami is complete lack of perfusion leading to. Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction. States, someone experiences an acute myocardial infarction (ami)—that adds up to about 600,000 amis every year.
However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction.
However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. Complications of ami lv aneurysm. Myocyte necrosis, interstitial edema, inflammation, and matrix. Complications of acute myocardial infarction. After an infarction, an obvious complication is a second infarction, which may occur in the domain of another atherosclerotic coronary artery, or in the same zone if there are any live cells left in the infarct. There are many ways to prevent complications.
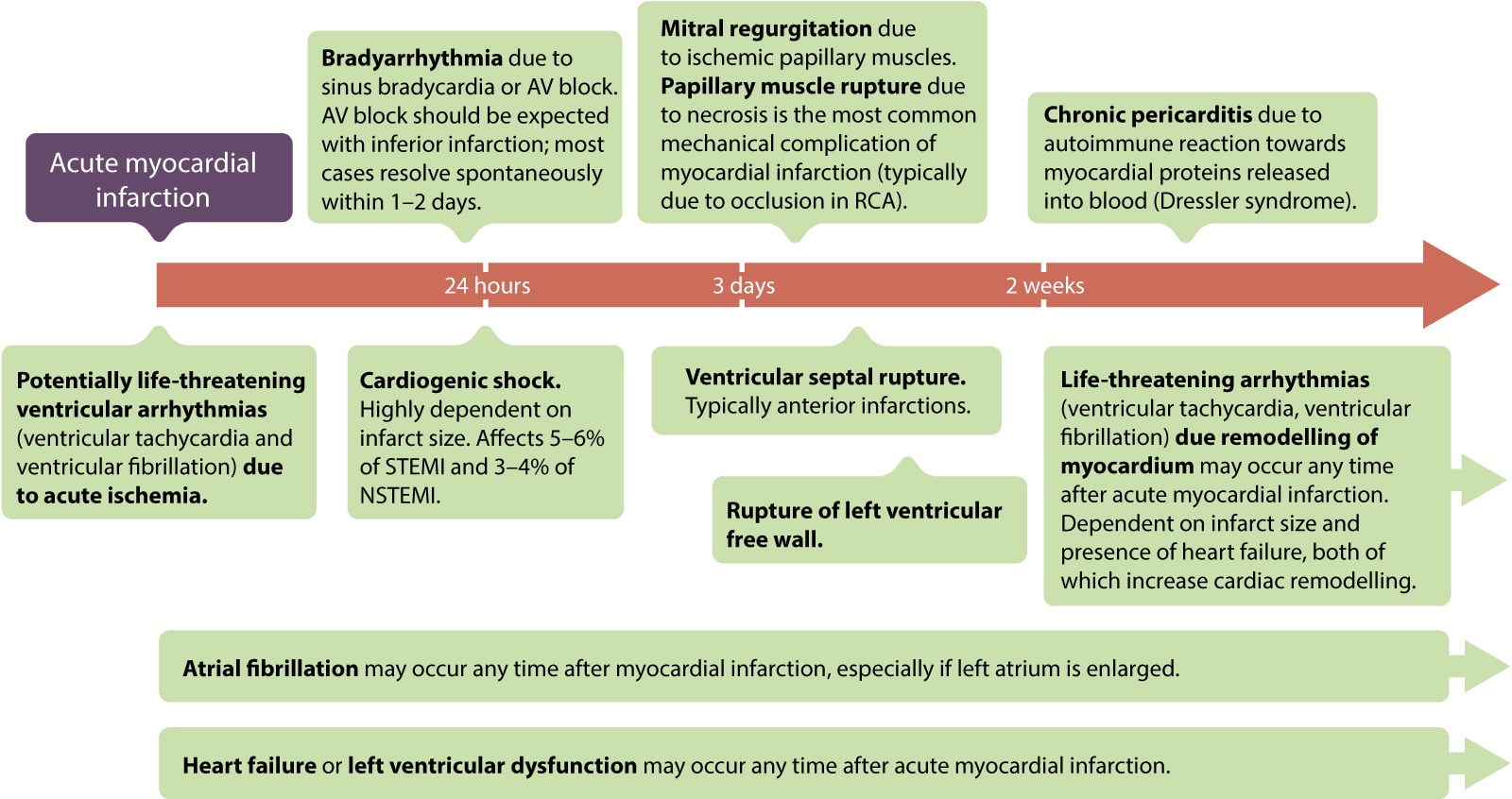 Source: ecgwaves.com
Source: ecgwaves.com
Describe complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami). In the chronic phase, negative remodeling and aneurysm formation may occur. There are many ways to prevent complications. Echocardiography is usually the first test used to identify the type, location, and hemodynamic consequences of the mechanical complication. States, someone experiences an acute myocardial infarction (ami)—that adds up to about 600,000 amis every year.
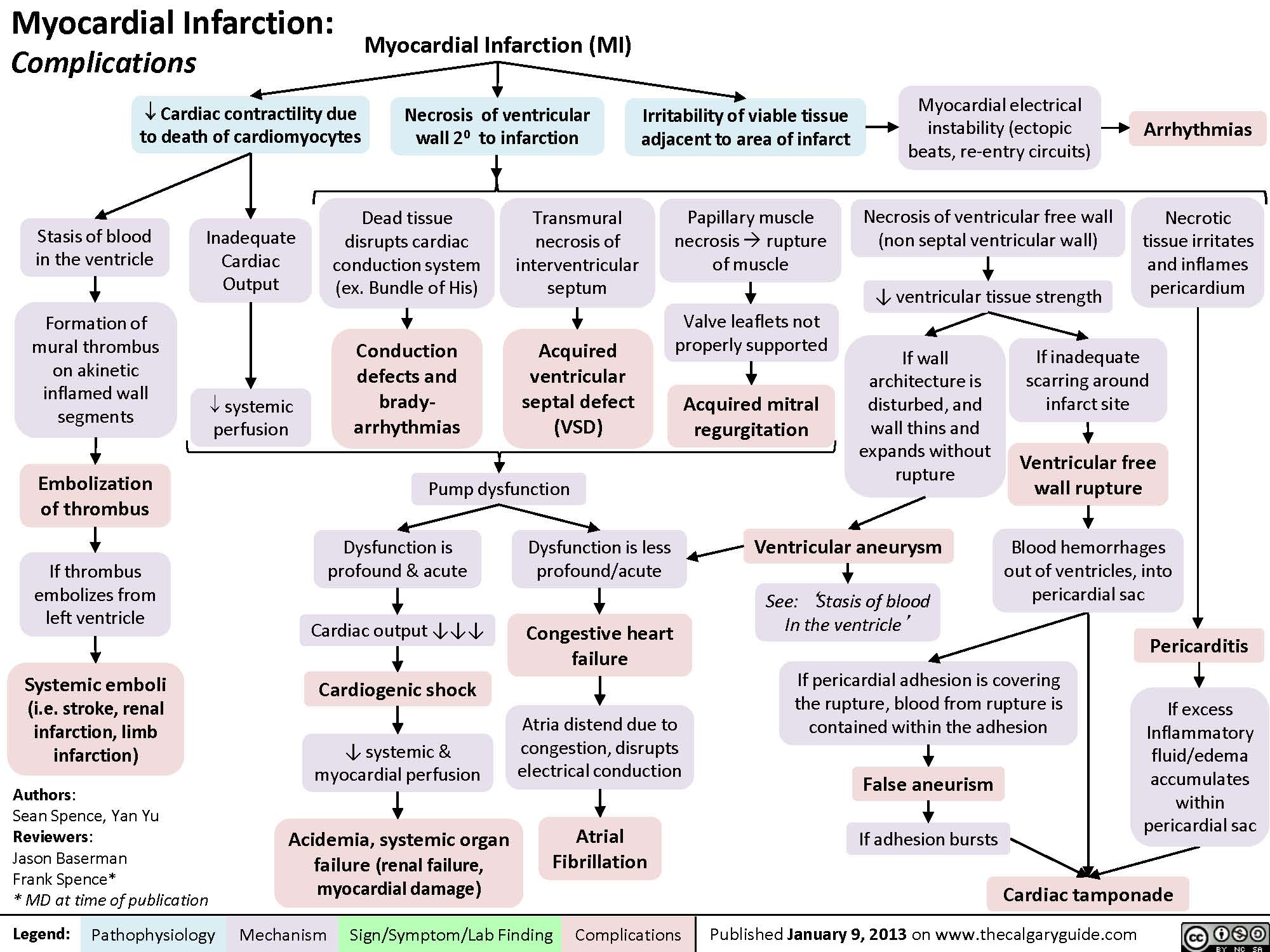 Source: calgaryguide.ucalgary.ca
Source: calgaryguide.ucalgary.ca
However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. The pathophysiological mechanism of mc post ami is complete lack of perfusion leading to. The author and planners of this cne activity have disclosed no relevant financial relationships with any commercial companies pertaining to this activity. An acute myocardial infarction is a heart attack. See the last page of the article to learn how to earn cne credit.
 Source: dailymeded.com
Source: dailymeded.com
Complications of acute myocardial infarction — diagnosis and treatment— jmaj 45(4): Cardiogenic shock or acute pulmonary edema are frequent presentations. Early reperfusion and medical therapy have drastically reduced ami An acute myocardial infarction is a heart attack. Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction.
 Source: cardioguide.ca
Source: cardioguide.ca
States, someone experiences an acute myocardial infarction (ami)—that adds up to about 600,000 amis every year. Echocardiography is usually the first test used to identify the type, location, and hemodynamic consequences of the mechanical complication. Learn about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of this life threatening condition. Acute mechanical complications of mi include sequelae from left or right ventricular systolic impairment or a loss of structural integrity that results in cardiac wall rupture, papillary muscle rupture, or ventricular septal rupture. See the last page of the article to learn how to earn cne credit.
 Source: jacc.org
Source: jacc.org
Occurs due to scarring and do not rupture. In the chronic phase, negative remodeling and aneurysm formation may occur. Describe complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami). All of these conditions could potentially lead to lv. Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins.
 Source: grepmed.com
Source: grepmed.com
Pseudoaneurysm is myocardial rupture contained by local area of pericardium. Complications of ami lv aneurysm. In this american heart association (aha) scientific statement, we (1) define the epidemiology of. Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction. Myocyte necrosis, interstitial edema, inflammation, and matrix.
 Source: grepmed.com
Source: grepmed.com
Describe complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami). Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (mi). In this american heart association (aha) scientific statement, we (1) define the epidemiology of. There are many ways to prevent complications. Complications of acute myocardial infarction — diagnosis and treatment— jmaj 45(4):
 Source: pinterest.dk
Source: pinterest.dk
Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami) are ventricular septal defect (vsd), papillary muscle rupture or dysfunction, cardiac free wall rupture, ventricular aneurysm, dynamic left ventricular (lv) outflow tract (ot) obstruction, and right ventricular (rv) failure. There are many ways to prevent complications. All of these conditions could potentially lead to lv. In the chronic phase, negative remodeling and aneurysm formation may occur. Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins.
 Source: grepmed.com
Source: grepmed.com
Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins. An acute myocardial infarction is a heart attack. Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami) are ventricular septal defect (vsd), papillary muscle rupture or dysfunction, cardiac free wall rupture, ventricular aneurysm, dynamic left ventricular (lv) outflow tract (ot) obstruction, and right ventricular (rv) failure. Describe complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami). However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Broadly, the latter share the same pathogenesis: Complications of lv aneurysm are chf, arterial embolism and ventricular arrhythmias. After an infarction, an obvious complication is a second infarction, which may occur in the domain of another atherosclerotic coronary artery, or in the same zone if there are any live cells left in the infarct. Cardiogenic shock or acute pulmonary edema are frequent presentations. Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction.
 Source: thoracickey.com
Source: thoracickey.com
Broadly, the latter share the same pathogenesis: In this american heart association (aha) scientific statement, we (1) define the epidemiology of. Broadly, the latter share the same pathogenesis: Describe complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami). The pathophysiological mechanism of mc post ami is complete lack of perfusion leading to.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
All of these conditions could potentially lead to lv. However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins. After an infarction, an obvious complication is a second infarction, which may occur in the domain of another atherosclerotic coronary artery, or in the same zone if there are any live cells left in the infarct. Complications of acute myocardial infarction — diagnosis and treatment— jmaj 45(4):
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The main mechanical complications (mc) of acute myocardial infarction are ventricular septal rupture (vsr), free wall rupture (fwr), and ischemic mitral regurgitation (imr). Complications of ami lv aneurysm. Cardiogenic shock or acute pulmonary edema are frequent presentations. Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins. Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (ami) are ventricular septal defect (vsd), papillary muscle rupture or dysfunction, cardiac free wall rupture, ventricular aneurysm, dynamic left ventricular (lv) outflow tract (ot) obstruction, and right ventricular (rv) failure.
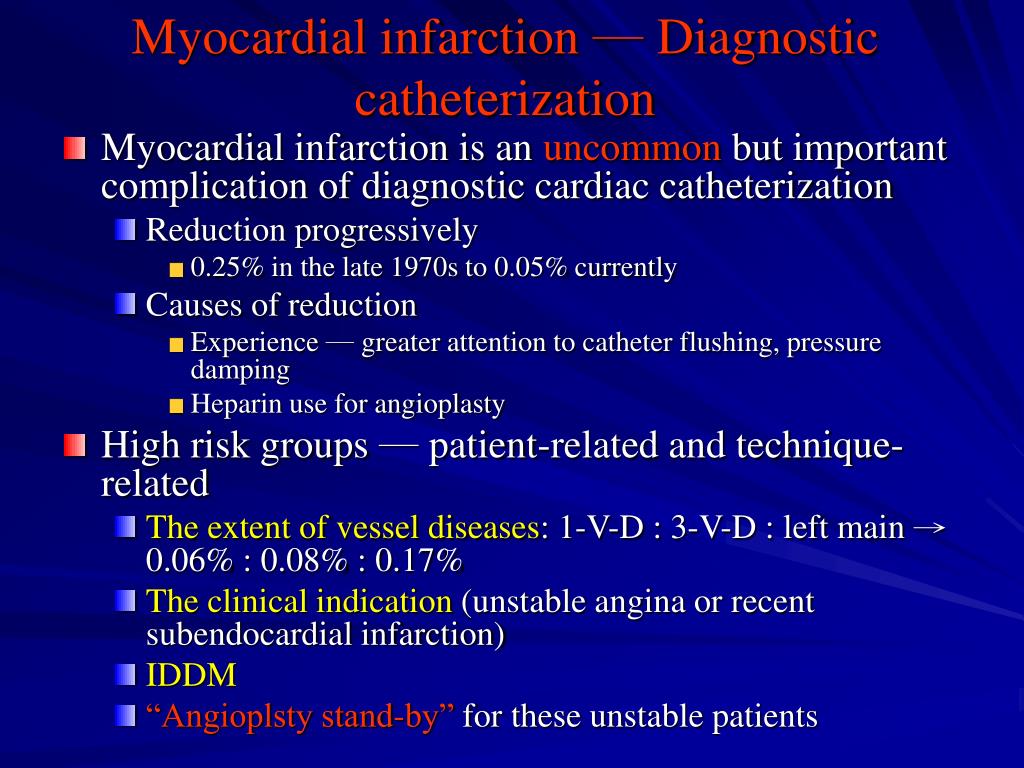 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. Complications may occur due to ischemic or injured tissue and therefore may begin within 20 minutes of the onset of m.i., when myocardial tissue injury begins. Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (mi). Myocardial infarction complications may occur immediately following a heart attack (in the acute phase), or may need time to develop (a chronic problem). Acute mechanical complications of mi include sequelae from left or right ventricular systolic impairment or a loss of structural integrity that results in cardiac wall rupture, papillary muscle rupture, or ventricular septal rupture.

Most complications present < 24 hours after an acute myocardial infarction (mi), but mechanical complications may occur anytime in the first week after an acute mi. Cardiogenic shock or acute pulmonary edema are frequent presentations. In the chronic phase, negative remodeling and aneurysm formation may occur. Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (mi). Myocardial infarction complications may occur immediately following a heart attack (in the acute phase), or may need time to develop (a chronic problem).
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (mi). The pathophysiological mechanism of mc post ami is complete lack of perfusion leading to. Rupture of the left ventricular free wall, rupture of the interventricular septum, and acute mitral regurgitation due to papillary muscle necrosis are three potentially lethal mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction (mi). Pseudoaneurysm is myocardial rupture contained by local area of pericardium. States, someone experiences an acute myocardial infarction (ami)—that adds up to about 600,000 amis every year.
 Source: accessanesthesiology.mhmedical.com
Source: accessanesthesiology.mhmedical.com
In the chronic phase, negative remodeling and aneurysm formation may occur. Echocardiography is usually the first test used to identify the type, location, and hemodynamic consequences of the mechanical complication. Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction. However, patients with large infarcts or those who do not receive timely revascularization remain at risk for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. All of these conditions could potentially lead to lv.
 Source: grepmed.com
Source: grepmed.com
Cardiogenic shock or acute pulmonary edema are frequent presentations. See the last page of the article to learn how to earn cne credit. In this american heart association (aha) scientific statement, we (1) define the epidemiology of. Complications of acute myocardial infarction — diagnosis and treatment— jmaj 45(4): Mechanical complications most commonly occur within the first week after myocardial infarction.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title complications of acute myocardial infarction by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.